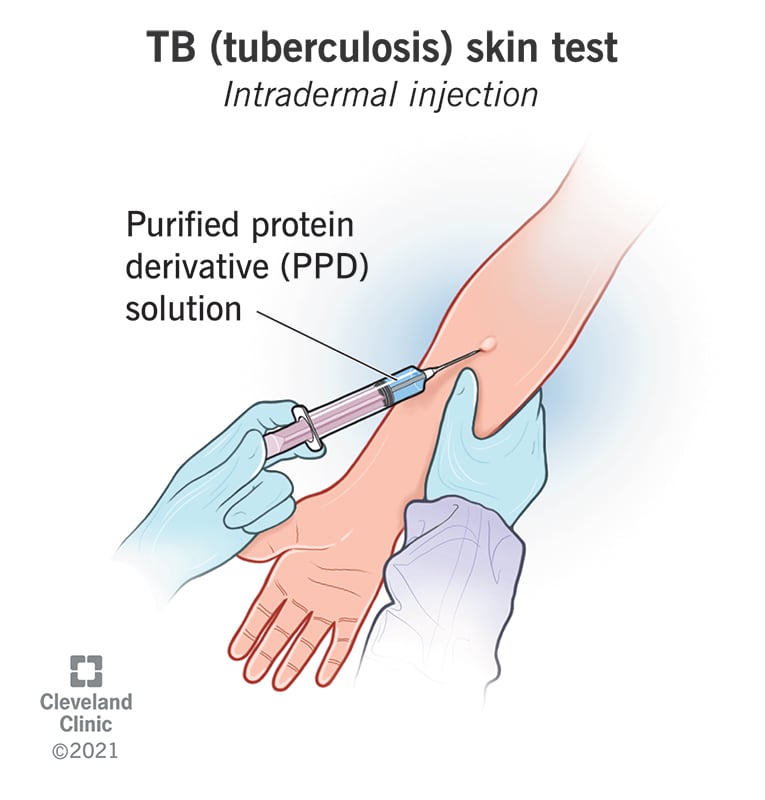
A general pediatrician can be a good choice if you are searching for a pediatrician who is experienced in all kinds of childhood diseases. You'll be introduced to Dr. Chiu (Dr. Shew), and Dr. Krummel (Dr. Krummel). All of these surgeons are members of the American Society of Pediatric Surgery and are experts in pediatric surgery. They are also professors of children's surgery at Stanford University School of Medicine.
Dr. Chiu is a pediatric surgeon.
Dr. Chiu was a primary care pediatrician at Martha Eliot Health Center, Watertown, MA, before joining the Sick Kids faculty. He loves working with the diverse inner city population. Additionally, he is the Perkins School for the Blind's medical director in Watertown MA. His research interests are in lymphocyte development, pediatrics, and other related topics. He is particularly interested, among other things, in pediatric cancer prevention and treatment, as well as child development and systems of care improvement.
Dr. Shew, a general pediatric surgeon, is available for consultation.
Dr. Stephen B. Shew practices as a pediatric (general), surgeon in Palo Alto. Dr. Shew is board-certified, and accepts most insurance plans. To make an appointment with Dr. Shew, patients should call his office or confirm their coverage information. His office will correct any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies. Please review the fee schedule to see if Dr. Shew accepts new patients.
Dr. Krummel is a general pediatric surgeon
Thomas Krummel, MD, is a general pediatric surgeon and has been a member of Sante Ventures' board of directors since 2014. He was awarded the William E. Ladd medal for 2020, which is the highest honor in pediatric surgical. He is a Stanford University professor of surgery and has over 35 years of expertise in the field. In addition to his current role, Dr. Krummel has served as a director of the general surgery residency program and as chair of the Department of Surgery.
Stanford University School of Medicine is Dr. Chiu's associate professor
Dr. Chiu obtained her MD from Queen's University in Canada. She completed her surgical training in the Gallie Program at the University of Toronto and completed a PhD in Immunology in the laboratory of Dr. Jayne Danska. Dr. Chiu completed her surgical and paediatric critical training at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto. She is currently an assistant professor of pediatric surgery at Stanford University School of Medicine.
Dr. Frist works as an associate professor at Stanford University School of Medicine
An active faculty member in the Department of Surgery at the University of Hawaii, Dr. Kaplan specializes in pediatric surgery and has been a member of the department for 25 years. He is also an associate professor of pediatrics and vice chair of research at the school. He received his medical education from the University of Wisconsin Madison. He also completed his general and pediatric surgical residencies with the University of Oklahoma. Before joining Stanford's faculty, he served as Chief of Pediatric Surgery at the Children's National Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
Dr. Dunn is a pediatric surgeon.
Dr. Stephen Dunn in Camden is a skilled pediatric surgeon. He practices at three medical centers and has extensive experience treating children of all ages. Dr. Dunn can speak Mandarin fluently, as well as English, Spanish and Mandarin. He is affiliated with many hospitals, including Stanford Hospital and California Pacific Medical Center. He is board certified, holds numerous professional honors, such as the American Board of Surgery’s Recognized Physicians Award.

Dr. Shew has been a Stanford University School of Medicine Senior Resident.
Dr. Shew has a clinical practice as well as active research interests. He is particularly interested in quality improvement and outcomes. He served as a leader on several hospital and university committees during his training. He also worked in research collaborations and multi-institutional quality.
FAQ
What are the three types of healthcare systems?
The first system is a more traditional system that gives patients little choice about who they see for treatment. They may go to hospital A for an operation but if not, they might just as well not bother.
The second system is a fee-for-service system where doctors earn money based on how many tests, operations, and drugs they perform. They won't do extra work if they don't get enough money. You will pay twice as much.
The third system uses a capitation system that pays doctors according not to how many procedures they do but what they spend. This encourages doctors use of less expensive treatments, such as talking therapies, instead of surgical procedures.
What does the term "health care" mean?
The delivery of services that promote good mental and physical health is called health care.
What does "public health" actually mean?
Public Health is the protection and improvement of the health of the community. Public health is the prevention of disease, injury, disability, promotion of good health, adequate nutrition, and control over communicable and environmental hazards as well behavioral risks.
Statistics
- The healthcare sector is one of the largest and most complex in the U.S. economy, accounting for 18% of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020.1 (investopedia.com)
- For the most part, that's true—over 80 percent of patients are over the age of 65. (rasmussen.edu)
- For instance, Chinese hospital charges tend toward 50% for drugs, another major percentage for equipment, and a small percentage for healthcare professional fees. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Consuming over 10 percent of [3] (en.wikipedia.org)
- The health share of the Gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to continue its upward trend, reaching 19.9 percent of GDP by 2025. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
What are the key segments of the healthcare industry?
The key segments of the healthcare industry include medical devices, pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, biotechnology, therapeutics, health information technology, medical equipment, etc.
Defibrillators, blood pressure monitors (defibrillators), stethoscopes, and ultrasound machines are some examples of medical devices. These products are used to diagnose and prevent or treat disease.
Pharmaceuticals are medicines that are prescribed to cure disease or relieve symptoms. These include antibiotics.
Diagnostics are tests that are performed by labs to diagnose illness or injury. Examples include blood tests, urine samples, CT scans, MRI scans, X-rays, etc.
Biotechnology refers to using living organisms (such as bacteria) to produce useful substances that can be applied to human beings. Examples include vaccines, insulin, and enzymes.
Therapeutics are medical treatments that treat diseases or alleviate symptoms. These treatments can include drugs, radiation therapy and surgical interventions.
Information technology for health is a category of computer software that helps physicians and their teams manage patient records. It helps doctors and their teams track which medications are being used, when they should have been taken, and if they work properly.
Equipment used in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of medical conditions or illnesses is called medical equipment. Examples include dialysis machines, pacemakers, ventilators, operating tables, etc.